#6
1)† †† Find the solution of the Poisson Equation
†††††††
††††††† ![]()
††††††† in
the domain![]() subject to the boundary conditions:
subject to the boundary conditions:
††††††† ![]() ,
, ![]() ,†
,† ![]() ,
, ![]()
2)† †† Sketch
the graph of the solution for† ![]() ,
, ![]() †and
†and
††††††† a)
††† ![]() , †††
, ††† ![]()
††††††† b)††† ![]() ,††††
,†††† ![]()
Feel free to modify the conditions, if you think that it improves the problem.
![]()
Solution:
![]()
I†††††† ††††††† Non-homogeneous equation with 2 homogeneous and 2 non-homogeneous boundary conditions.
Use the superposition principle to reduce the problem to set of basic problems (4.6.2 7-8, pp. 284-285):
1)†††† ![]()
††††††† in
the domain![]() subject to the boundary conditions:
subject to the boundary conditions:
††††††† ![]() ,
, ![]() ,†
,† ![]() ,
, ![]()
2)†††† ![]()
††††††† in
the domain![]() subject to the boundary conditions:
subject to the boundary conditions:
††††††† ![]() ,
, ![]() ,†
,† ![]() ,
, ![]()
3)†††† ![]()
††††††† in
the domain![]() subject to the boundary conditions:
subject to the boundary conditions:
††††††† ![]() ,
, ![]() ,†
,† ![]() ,
, ![]()
Then the total solution will be:
![]()
![]()
II†††††††††††† Solution of the basic problems:††††††††
1)††† Separation of variables:††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††† ![]() †††
††† ![]() †††
††† ![]()
††††††† Sturm-Liouville Problem (equation with two homogeneous b.c.):
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††
††††††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††
††††††††††† ![]() ††† †††††††††††††††††††††††
††† ††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]()
††††††† Second equation:
††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]()
††††††† Use shifted form of solution:
††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††† ![]()
††††††† Apply ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]() †
† ![]()
††††††† Therefore
††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]()
††††††† Write the solution in the form of infinite series:
††††††† ![]()
![]()
††††††† Apply the last
b.c. to determine coefficients ![]() :
:
††††††† ![]()
![]()
Treat it as the cosine Fourier
series expansion of function ![]() , then coefficients are:
, then coefficients are:
![]() †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]() †
† ![]() †††††††††††
†††††††††††
![]() ††
†† ![]() †
† 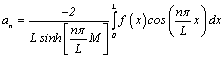
Then solution is:
††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]()
††††††††††††††††††††††† 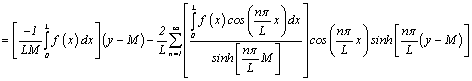
2)††† Separation of variables:††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††† ![]() †††
††† ![]() ††††††
†††††† ![]()
††††††† Sturm-Liouville Problem (equation with two homogeneous b.c.):
††††††† ![]() ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††† ![]() ††††††††††††††
†††††††††††††† ![]() †††††††††††
††††††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]() ††
†† ![]()
††††††† ![]()
††††††† Second equation:
††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]()
††††††† The solution:
††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††† †††††††
†††††††††††††† ††††††† ![]()
††††††† ![]()
††††††† Apply ![]()
![]() †
† ![]()
††††††† Therefore
†††††††
††††††† ![]()
††††††† Write the solution in the form of infinite series:
††††††† ![]()
![]()
††††††† Apply the last
b.c. to determine coefficients ![]() :
:
††††††† ![]()
![]()
Treat it as the sine Fourier
series expansion of function ![]() , then coefficients are:
, then coefficients are:
†††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
![]() ††
†† ![]() †
† 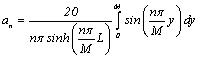
Then solution is:
††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]()
††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††† 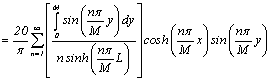
3)† Poissonís Equation
![]() Sturm-Liouville
Problem for X:
Sturm-Liouville
Problem for X:
![]() †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]() ††††††††††
†††††††††† ![]() ††††††††††
†††††††††† ![]()
![]() †††††††††††
††††††††††† ![]() †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]() ††††††
†††††† ![]() ††††††
†††††† ![]()
![]()
Sturm-Liouville Problem for Y:
![]() ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††††††
![]() ††††††††††††††
†††††††††††††† ![]() †††††††††††
††††††††††† ![]() ††††††††††
†††††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]() ††††††††††
†††††††††† ![]()
![]()
Solution:
![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]() †††††††
††††††† ![]()
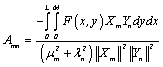 †††††††††
††††††††† 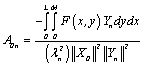
Then the solution is:
![]()
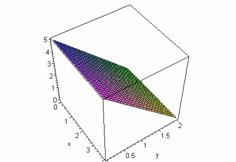
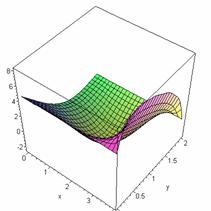
The graph of solution
for the case a):
![]() , †††
, ††† ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
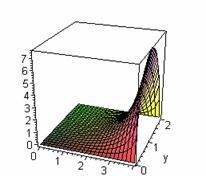
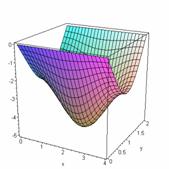
![]()
Solution for case b) see
in the Maple example.