#16
a) Reduce the following BVP to Sturm-Liouville problem:
![]()
![]()
and find eigenvalues and eigenfunctions .
b) Use the obtained set of eigenfunctions for generalized Fourier series representation of the
function
![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]()
Sketch the
graph for ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]()
Solution:
The 2nd
order ODE includes parameter![]() .
.
We have to find the
values of this parameter (![]() )
)
for which ODE with
boundary conditions has non-trivial solution ![]() .
.
The existence of
such solution is provided by the Sturm-Liouville Theorem (4.5.3 p.268).
1) Reduce
our BVP to SLP:
Rewrite equation in
self-adjoint form with the help of the multiplication factor (4.5.4 Eq.19
p.271):
Identify
coefficients
![]()
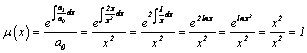
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (self-adjoint form, Eq.5)
(self-adjoint form, Eq.5)
![]() (operator
form, Eq.13)
(operator
form, Eq.13)
![]() (both
conditions are of the Dirichlet type)
(both
conditions are of the Dirichlet type)
According to Sturm-Liouville Theorem, this SLP has
infinitely many positive eigenvalues ![]() for which
for which
boundary value problem has non-trivial solution ![]() (eigenfunctions).
(eigenfunctions).
2) Find eigenvalues and eigenfunctions (solve BVP)
![]()
![]()
2nd order ODE, homogeneous, with variable coefficients, linear, Euler-Cauchy type
Auxiliary equation (see table “linear o.d.e.” Euler-Cauchy Equation):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
case 1 ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
general solution ![]()
apply boundary conditions:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Rewrite as a system in matrix form:
![]()
![]() because
because ![]()
Therefore, system has only the trivial solution
![]()
which yields the
trivial solution of BVP.
Therefore, there is
no eigenvalues in the interval
![]()
case 2 ![]()
![]()
general solution ![]()
apply boundary conditions:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
It also yields the trivial solution.
case 3 ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
general solution ![]()
apply boundary conditions:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
non-trivial solution only if
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]() eigenvalues
eigenvalues
![]() eigenfunctions
eigenfunctions
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
b) Generalized Fourier series expansion:
![]()
![]()
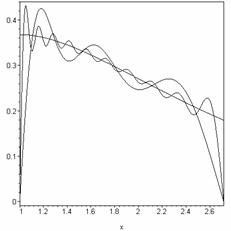
Maple example for ![]() :
:
> f:=x*exp(-x);
![]()
> u[n]:=sin(n*Pi*ln(x))/sqrt(x);
![]()
> N2[n]:=int(u[n]^2,x=1..exp(1));
![]()
> c[n]:=int(f*u[n],x=1..exp(1));
![]()
> f5:=sum(c[n]*u[n]/N2[n],n=1..5):
> f20:=sum(c[n]*u[n]/N2[n],n=1..20):
> plot({f,f5,f20},x=1..exp(1),axes=boxed,color=black);