4.5.0
BANACH AND HILBERT SPACES
1.
Normed Space Norm is a map ![]() such that for all
such that for all ![]() and
and ![]()
1. ![]()
![]() if and only if
if and only if ![]()
2. ![]()
3. ![]() (triangle
inequality)
(triangle
inequality)
Example:
in space ![]() of all continuous
functions in
of all continuous
functions in ![]()
norm can be defined as
![]()
2.
Metric Space Vector
space ![]() is a metric space if there exists
is a metric space if there exists
a
function ![]() such that for all
such that for all ![]()
1. ![]()
![]() for
for![]()
2. ![]() (symmetry)
(symmetry)
3. for all ![]() (triangle
inequality)
(triangle
inequality)
![]() is called the distance between
is called the distance between ![]() .
.
Vector
space with introduced metric is called a metric space.
In the normed vector space the metric can be introduced as
![]()
3.
Inner Product Inner product is a map![]() such that for all
such that for all ![]()
1. ![]() (
(![]() )
)
2. ![]()
![]()
3. ![]()
![]() if and only if
if and only if ![]()
Vector
space with introduced inner product is called an inner product
space. In inner product space the norm can be defined as
![]() for all
for all ![]()
4. Convergence Let
![]() be normed (metric space) and let
be normed (metric space) and let ![]() ,
, ![]()
The
sequence ![]() converges to
converges to ![]() if
if
![]() as
as ![]()
![]()
The
sequence ![]() is called the Cauchy sequence (convergent in
is called the Cauchy sequence (convergent in
itself) if
![]() as
as ![]() and
and ![]()
The
vector space ![]() is called complete if all its Cauchy sequences
are
is called complete if all its Cauchy sequences
are
convergent
in ![]() .
.
A complete normed space is called the Banach space. For example,
![]() is a Banach space with
is a Banach space with
![]() .
.
A complete inner product space is called a Hilbert space.
5. Orthogonality In the inner product space ![]() are called orthogonal if
are called orthogonal if ![]() .
.
If
set ![]() consists
of mutually orthogonal vectors,
consists
of mutually orthogonal vectors, ![]()
when
![]() , then this set is called an orthogonal set.
, then this set is called an orthogonal set.
If
in addition, ![]() , then set
, then set ![]() is called
orthonormal.
is called
orthonormal.
Orthogonal set is linearly independent set.
If
set ![]() is
linearly independent then it can be converted to the
is
linearly independent then it can be converted to the
orthonormal
set ![]() with the
help of the so called Gram-Schmidt
with the
help of the so called Gram-Schmidt
orthogonalization process:

Gram-Schmidt process ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
This algorithm can be formalized with the help of Gram’s determinant:
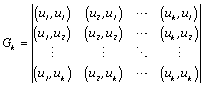 ,
, ![]()
Orthonormal vectors are detrmined by the formula
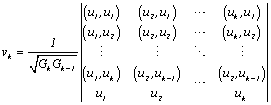
![]()
The
orthonormal set ![]() is said to be complete if there does not
is said to be complete if there does not
exist
a vector ![]() ,
, ![]() such that it is
orthogonal to all vectors
such that it is
orthogonal to all vectors
from
![]() .
.
6. Fourier Series Let
![]() be an orthonormal set.
be an orthonormal set.
![]() is called the Fourier series (generalized
Fourier series)
is called the Fourier series (generalized
Fourier series)
![]() are called the
Fourier coefficients,
are called the
Fourier coefficients, ![]()
Theorem The Fourier series![]() is convergent to the
is convergent to the
function![]() if and
only if
if and
only if
![]() (Parseval’s
equation)
(Parseval’s
equation)
Proof: Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ■
■
Let
![]() be an orthonormal set
.
be an orthonormal set
.
If for any ![]() its Fourier series
its Fourier series
![]()
converges
to ![]() in
in ![]() , then
, then ![]() is said complete in
is said complete in ![]() .
.
7.
Vector Space ![]() Consider
a particular case of Equation 3.3 from Definition 3.13 (p.205),
Consider
a particular case of Equation 3.3 from Definition 3.13 (p.205),
with
![]() and interval
and interval![]() :
:
![]()
Inner
product in vector space ![]() : For
: For ![]() define:
define:
![]() inner product in
inner product in ![]()
![]() weighted inner product in
weighted inner product in ![]()
with
the weight function ![]()
Inner
product vector space ![]() belongs to the class of Hilbert spaces.
belongs to the class of Hilbert spaces.
Introduced
inner product induces the norm in ![]() :
:
![]()
![]()
Historically, the first complete set was used by Fourier set of trigonometric functions
![]() ,
, ![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]() .
.
The complete orthogonal sets used in the solution of PDE will be
generated by the solution of the Sturm-Liouville problems.
8. Exercizes: The
set of monoms ![]() is linearly
independent in
is linearly
independent in ![]() .
.
a) Using the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization algorithm with inner product
![]()
construct
an orthonormal set in ![]()
(the obtained set will be the set of the Legendre polynomials up the the scalar multiple).
b) Using the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization algorithm with inner product
![]()
construct
an orthonormal set in ![]()
(the obtained set will be the set of the Tchebyshev polynomials up the the scalar multiple).
c) Use the obtained orthonormal sets for generalized Fourier series expansion of the function:
![]()
Compare
the results for truncated series with 2,3,4 terms. Make some observations.
The Scottish Cafe in Lvov
The original Szkocka Café (Scottish Café)
in
(on the left, shown at the time when it was
the Dessert Bar at Shevchenko Prospekt 27)
Now is a Bank (on the right).
The café was a
meeting place for many mathematicians including Banach, Steinhaus, Ulam, Mazur,
Kac, Schauder, Kaczmarz and others.
Problems were
written in a book kept by the landlord and often prizes were offered for their
solution.
A collection of these problems appeared later
as the Scottish Book.
R D Mauldin, The
Scottish Book, Mathematics from the Scottish Café (1981) contains the
problems as well as some solutions and commentaries.